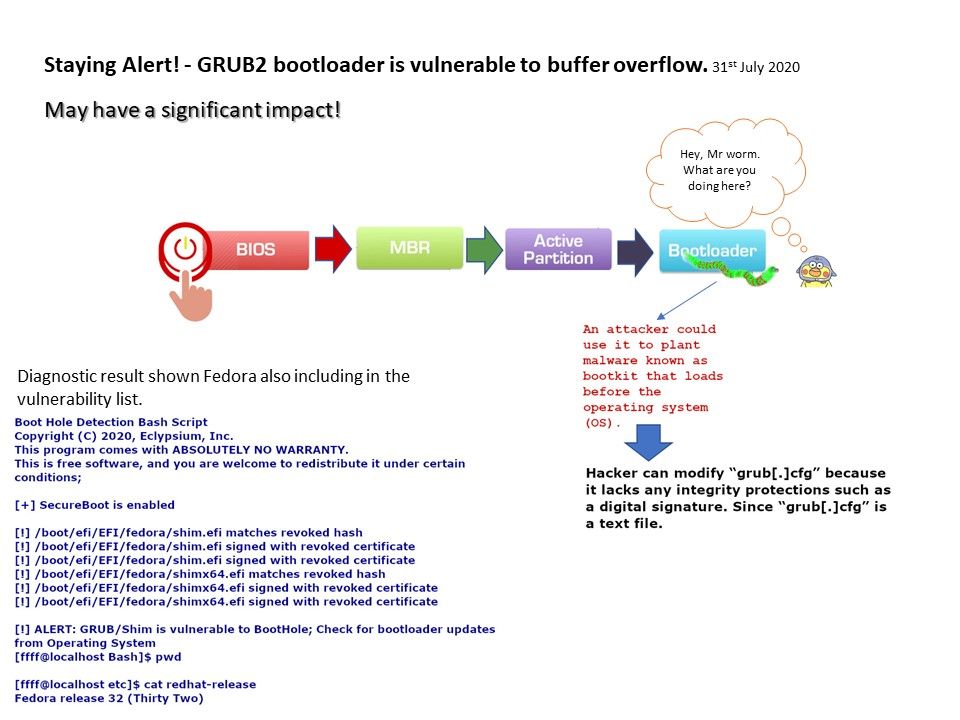
1.3.6 Boot Loader Configuration for UEFI-Based PXE Clients

Ubuntu Macbook
The grub.cfg file is the default boot loader configuration file for UEFI-based PXE clients and uses GRUB 2 configuration settings:
The linuxefi directive defines the name of the kernel executable and defines any parameters that should be appended when loading the kernel, such as the location of the installation packages, and how to access these packages. This example uses HTTP to install the packages from the specified URL. The initrdefi directive defines the name of the ram-disk image.
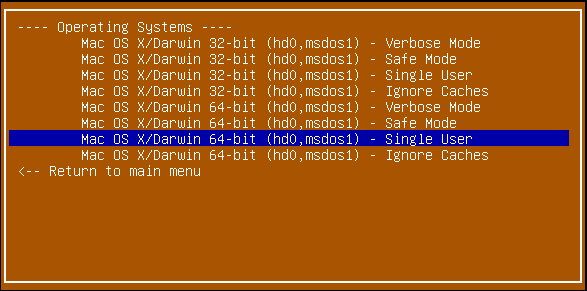
Grub2 Macbook
- Super GRUB 2 Disk—Download this handy CD image from its home page. Be sure to get Super GRUB 2 Disk, not Super GRUB Disk. Burn the disc image like you burned the Ubuntu install disc image, or copy it to a second USB flash drive. REFInd—This is a fork of the earlier rEFIt Mac boot manager. It's part of the boot process as described on this.
- GNU GRUB (GRand Unified Bootloader) is a free and open source project that provides users with an easy-to-install-and-configure boot loader software for booting a single or multiple operating systems that are installed on a personal computer or laptop. Key features include.
- Grub on Mac via EFI (Linux: /dev/sda1 Darwin: /dev/disk0s1) (MacBook Pro Early 2011 if it matters) 1. Triple Boot Mac OS Sierra, Windows 10, Kali Linux 2.0 On A Macbook Pro. Install Windows 10 or 8.1 on MacBook 4,1. 3.Complete. recipe for installing single-boot Linux.
01-MACaddress (for example, grub.cfg-01-80-00-27-c6-a1-16) Full 32 bits of the IP address (for example, grub.cfg-0A0000FD) Most significant 28 bits of the IP address (for example, grub.cfg-0A0000F) Most significant 24 bits of the IP address (for example, grub.cfg-0A0000). Grub2Win is completely free, open source software. All modules are digitally signed for your security. Safely boot multiple Windows and Linux systems on both GPT and MBR disks. Supports both 64 and 32 bit EFI firmware as well as BIOS.
The kernel and ram-disk image file paths are assumed to be relative to the subdirectory that contains the boot loader, for example efi. If you place the vmlinuz and initrd.img files in a subdirectory such as efi/OL7, ensure you have the correct relative paths.
By default, GRUB 2 does not provide any indication that is transferring the kernel and ram-disk images files. The echo statements in the example above provide a simple indication of progress.
To support different types of client, you can create a configuration file named grub2.cfg- where client-IDclient-ID
A client's MAC address prefixed by
01-, which represents the ARP hardware type for Ethernet, and using dashes to separate each byte value instead of colons (for example,01-80-00-27-c6-a1-16).The file name must use lowercase characters for the MAC address.
A client's IP address expressed in hexadecimal without any leading 0x (for example,
0A0000FDrepresents the IP address 10.0.0.253).To reduce the number of configuration files, you can group clients by IP address range, for example
0A0000Erepresents the IP address range 10.0.0.224 through 10.0.0.239.
Place the configuration files in the same directory as the boot loader files, for example efi.
The boot loader looks for a configuration file in the following order until it finds a matching file name:
01-(for example,MAC_addressgrub.cfg-01-80-00-27-c6-a1-16)Full 32 bits of the IP address (for example,
grub.cfg-0A0000FD)Most significant 28 bits of the IP address (for example,
grub.cfg-0A0000F)Most significant 24 bits of the IP address (for example,
grub.cfg-0A0000)Most significant 20 bits of the IP address (for example,
grub.cfg-0A000)Most significant 16 bits of the IP address (for example,
grub.cfg-0A00)Most significant 12 bits of the IP address (for example,
grub.cfg-0A0)Most significant 8 bits of the IP address (for example,
grub.cfg-0A)Most significant 4 bits of the IP address (for example,
grub.cfg-0)grub.cfg(the default configuration file)
If several configuration files have identical content, you can use the ln command to link the files to a primary copy, for example:
For more information about GRUB 2, enter the info grub command to access the GRUB 2 manual.
For information about configuring and using kickstart to perform automated installation, see Section 3.2, “Automated Installation Using Kickstart”.
Grub2 For Mac Os

Grub2 For Mac Iso
Copyright © 2014, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. Legal Notices